http://www.spacecenter.dk/research/sun-climate/climate-debate-and-faq/climadebate-and-faq
What is climate research at the DNSC?
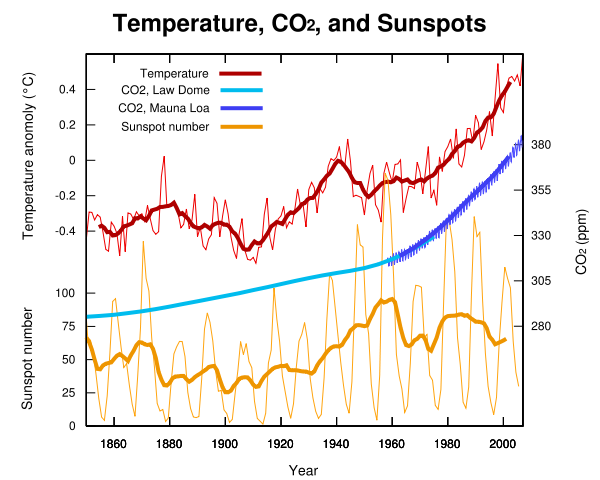
The Earth’s climate is always changing. This has been the case in the geological and historical time and even during the last 150 years, where systematic climate measurements have been made, we have seen clear climate changes.
Climate changes have both a scientific and a social perspective. The social perspective is associated with the range of climate change that can be attributed to the increasing human induced contribution. The scientific perspective is an endeavour to understand the full complex system of the various sources of climate change and their mutual interactions.
The Danish National Space Center, DNSC, comprises the country's largest collected expertise in the scientific disciplines that play a major and documented role in the understanding of climate change both in geological and historical time, namely variations in solar activity. DNSC regards it essential that this collected expertise is being used in an attempt to understand the natural causes of climate change in order to evaluate the contribution of natural causes to global change. Taking into account the large uncertainty associated with the estimated human contribution, a good research based estimate of the range of natural climate variations is an essential information.
DNSC is basing its effort in this area on own scientific results – observational, experimental, and theoretical. The scientific results have been published internationally and indicate that the varying activity of the Sun is indeed the largest and most systematic contributor to natural climate variations. The effect goes through solar modulation of the cosmic radiation, which affects the formation of aerosols and thereby also the formation of clouds. Even though a physical mechanism connecting cosmic rays to aerosol formation has been found experimentally, no climate model has yet made an attempt to include such an effect.
That there exists a significant contribution from solar activity variations to global temperature increase does not, however, exclude other contributions to the rising global temperature, natural as well as human. DNSC, however, is focused on establishing the best possible and scientifically based evaluation of the size of solar induced effects on climate.
Why is the climate changing?
Climate is subject to influences by both natural and human forces, including greenhouse gases, aerosols, solar activity, and land use change. The climate system is extremely complex and any estimate of the human contribution to climate change is very uncertain.
What are the natural causes to climate change?
Changes in the Sun contribute to climate change. Solar activity has been exceptionally high in the 20th century compared to the last 400 years and possibly compared to the past 8,000 years. When solar activity is high, the flux of galactic cosmic rays is reduced due to increased magnetic shielding by the Sun. The cosmic rays may influence Earths climate through formation of low lying clouds.
How can cosmic rays influence cloud formation?
Cosmic rays ionize the atmosphere and an experiment performed at the Danish National Space Center has found that the production of aerosols in a sample atmosphere with condensable gases (such as sulphuric acid and water vapor) depends on the amount of ionization. Since aerosols work as precursors for formation of cloud droplets, this is an indication that cosmic rays affect climate.
Climate models only include the effects of the small variations in the direct solar radiation (infrared, visible and UV). The effects of cosmic rays on clouds are not included in models and the models do a rather poor job of simulating clouds in the present climate. Since cloud feedbacks are a large source of uncertainty, this is a reason for concern when viewing climate model predictions.